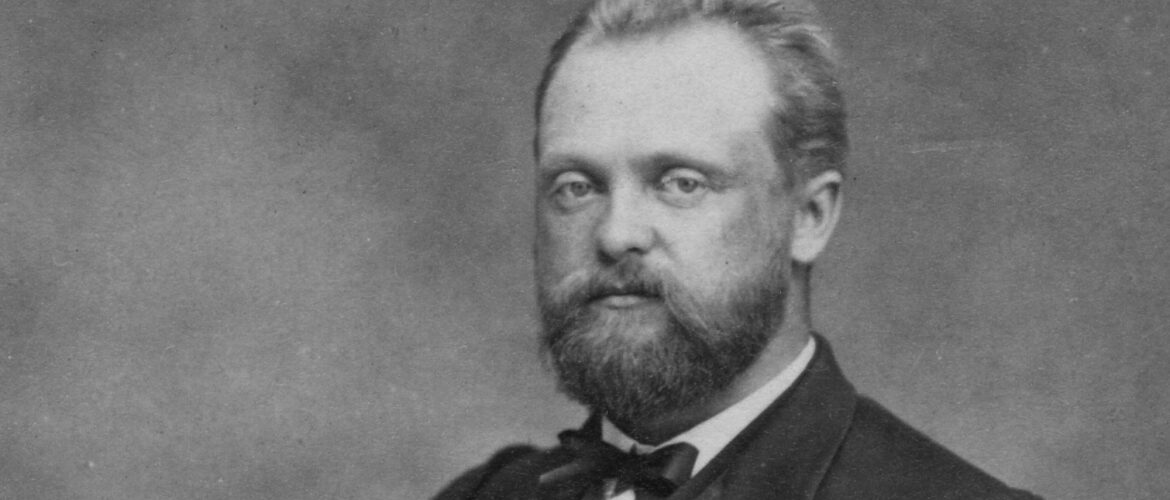
1831-1897.
Doctors.
Frithiof Holmgren established Sweden's first physiological laboratory in 1862 and became the country's first professor of physiology at the age of 33. He was also one of the most prominent teachers of his time at Uppsala University.
He became a world-famous scientist with the discovery of the retinal blood flow in the eye.
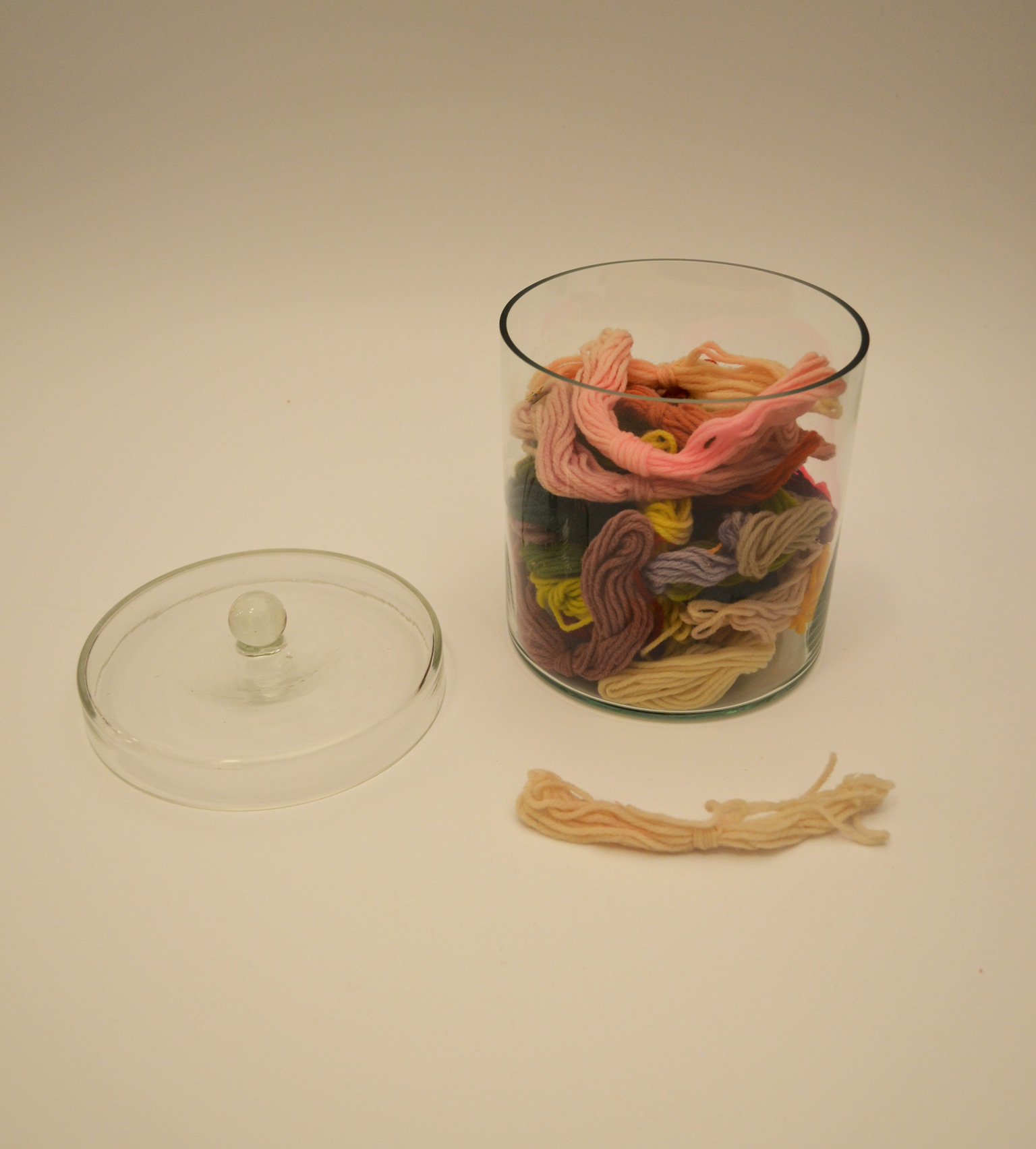
The studies of color blindness made Holmgren internationally known and in 1874 he described his method of using differently colored "sequined dolls", the so-called wool yarn test, to detect color blindness.
The method was of great practical importance for people in signal service, such as railway staff and seamen. A train accident in Lagerlunda in 1875 was suspected to have been caused by the inability of a dead engineer to distinguish between red and green. No one had considered that color vision could be important for railway personnel.
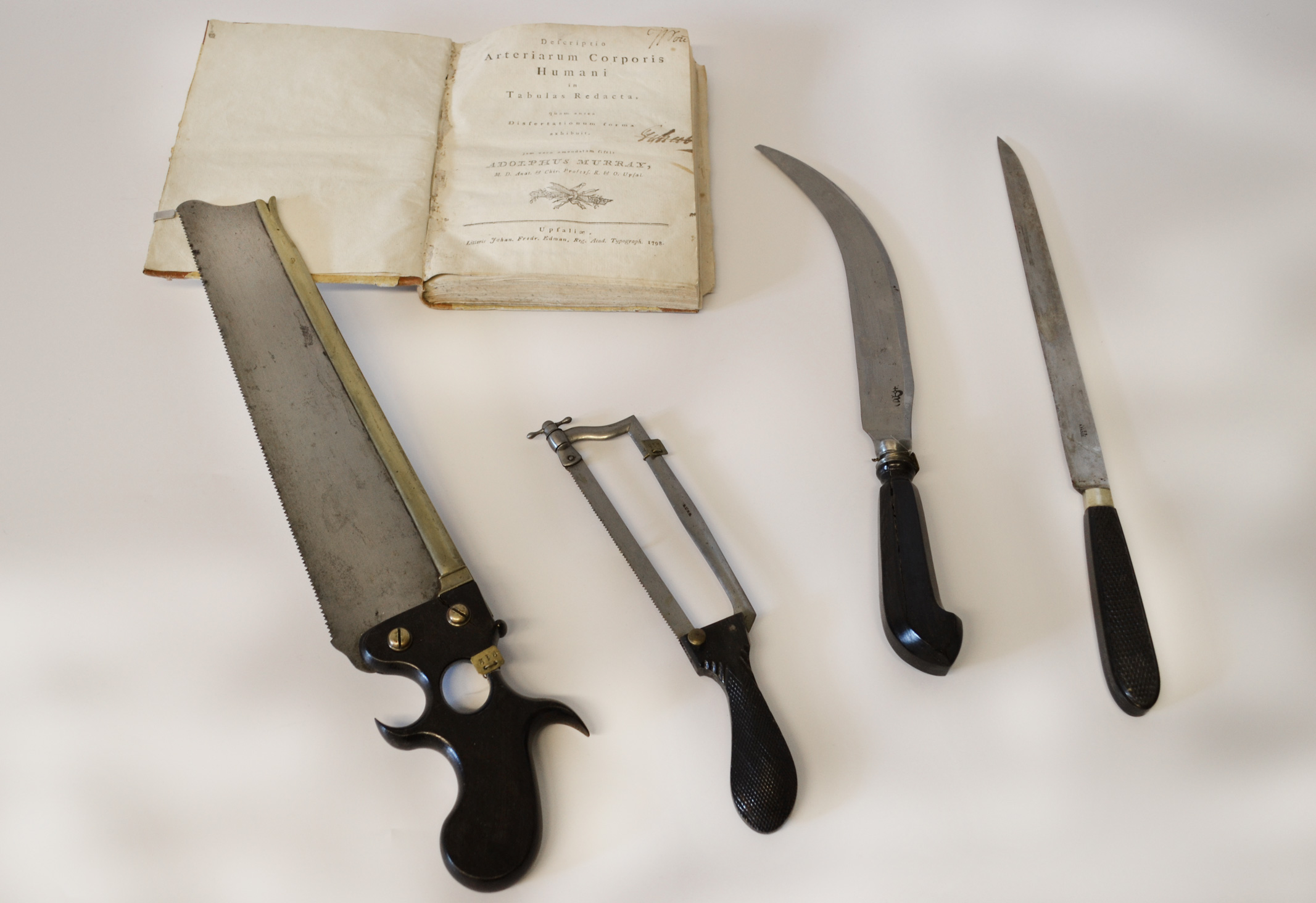
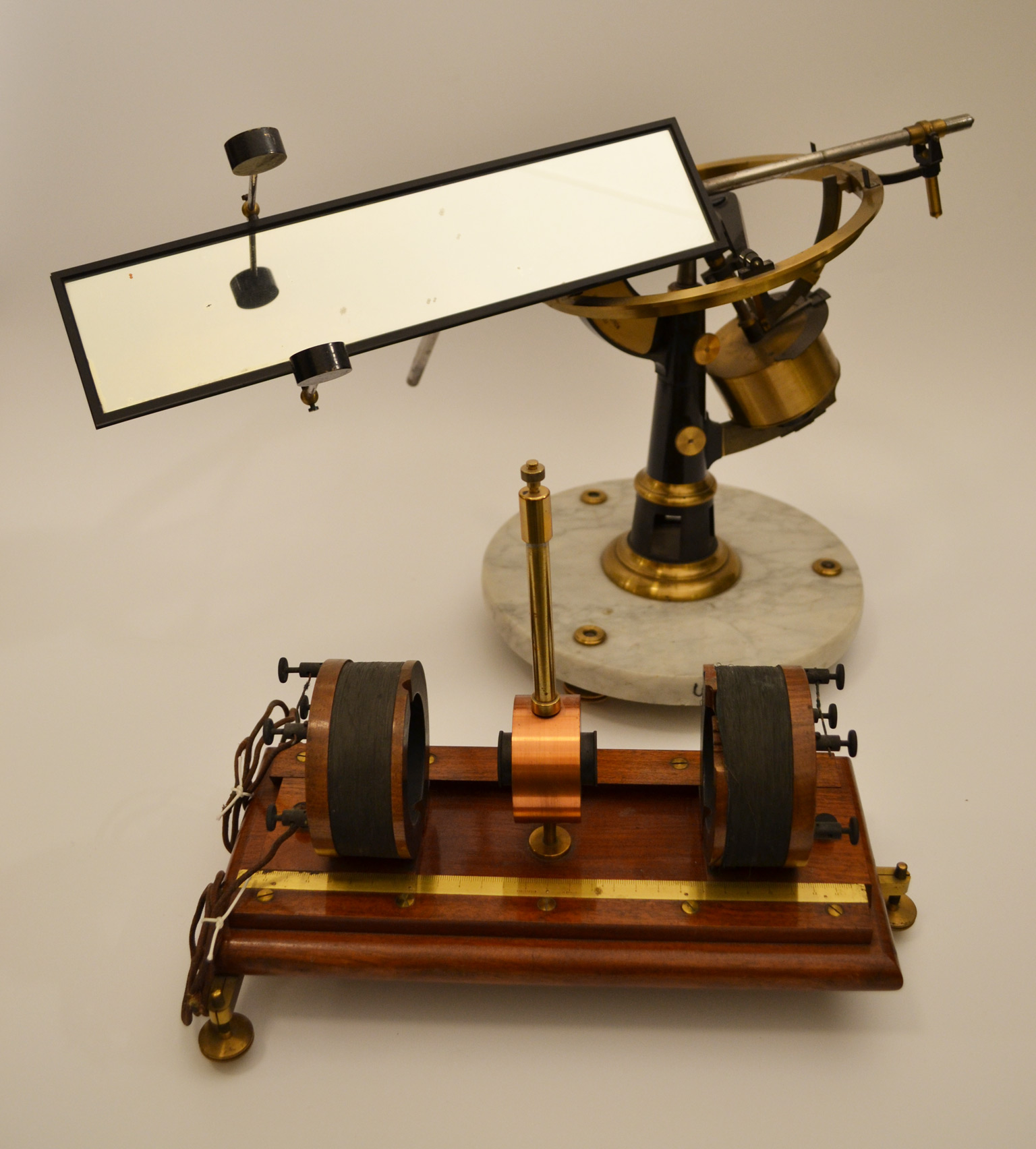
The equipment used by Holmgren to discover the retinal current, the electrical response of the retina to light. The equipment consists of a mirror galvanometer and a light catcher with a clockwork that drives the mirror. Photo: Museum of Medical History in Uppsala.
A more macabre study undertaken by Holmgren focused on whether beheading was a painless method of execution. Holmgren therefore attended four beheadings to examine the method from a physiological point of view. According to Holmgren, the case studies showed that beheading as a method met the requirements of painlessness. When the study was completed, he was also present at the execution of the so-called Alfta murderer in Gävle in 1893.
Holmgren also participated in the debates in Verdandi, and his radical stance was reflected in his dictation to the minutes of the consistory:
"I hold freedom of thought to be one of man's most precious privileges, and the university in which the principle of freedom of thought is not paramount does not, in my opinion, fulfill its task. To educate the young people studied to become thinking men should, in my opinion, be one of the main tasks of the university".
Frithiof Holmgren also emphasized the importance of physical education and founded the Studenternas Sharpshooting Association, the Studenternas Gymnastics Association and was chairman of the folk dance association Philochoros and promoter of the Uppsala Swimming Society.
Burial site: 0125-1141
Image description: Frithiof Holmgren, year unknown. Photo: Unknown photographer / UUBThe image is cropped]
Click here for an uncropped image