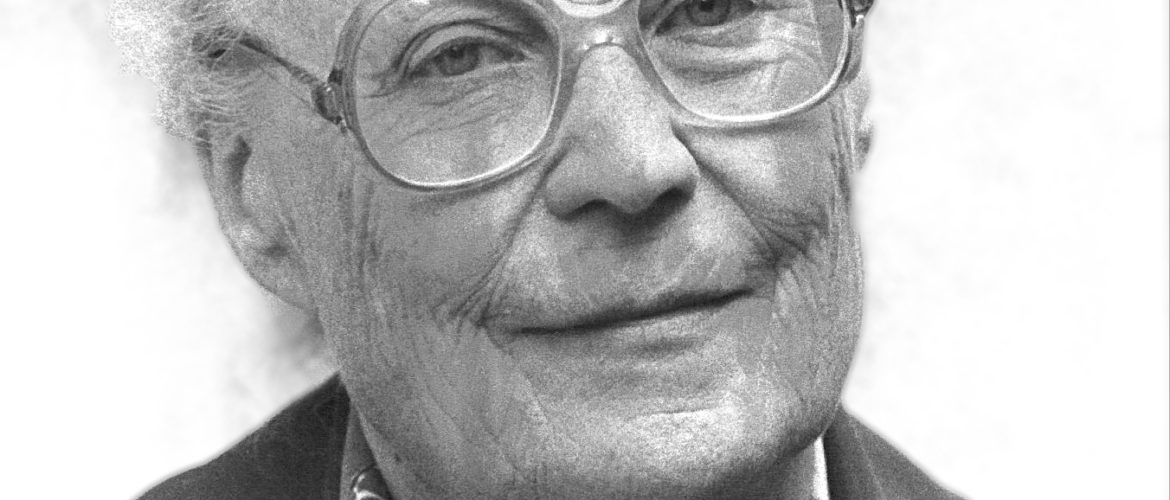
1948–2017.
Doctor, scientist and educator.
The first four years Hans Rosling lived in the district of Luthagen and then moved the family to the Svartbäcken district in Uppsala. After graduation, Rosling studied statistics and medicine at Uppsala University. The interest in public health science led, during a trip in Asia 1972, to a course in social medicine at St. Johns Medical College in Bangalore, India.
After a medical degree in 1975 and work as an AT-doctor in Hudiksvall, he trained further and acquired competence in the centre of Medicine at Uppsala University in 1977.
During the years 1979-1981 the spouses worked in Nacala Porto in northern Mozambique, where Hans was a district doctor and his wife, Agneta was midwife. In the Nacala district, an epidemic erupted in 1981, of a previously unknown spasmodic paralysis, with over 1 500 victims, whereof most women and children. The paralysis was linked to a highly poor and highly one-sided diet consisting of a toxic form of manioc (cassava).
Rosling described the disease in his doctoral thesis and named it Konzo. This means "bound bones" in the Congolese language where the disease was once described in 1938. During the 1980s, there were several outbreaks of Konzo in other African countries.
During the years 1983-1996, Rosling worked as a teacher and researcher at Uppsala University in collaboration with several universities in Africa and Asia. He was appointed in 1997 Professor of International Health at Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm.
in 1999 Rosling began lecturing with a new kind of animated bubble chart that showed the World's Socio-economic state and development over time. The program was called Trendalyzer and had been developed by his son and son's wife, with whom he co-founded the Gapminder Foundation.
The lectures made complicated statistics about the World's development comprehensible to the general public, decision makers and opinion-formers. The lectures spread through web and TV worldwide, and governments and organizations hired him as a lecturer and advisor.
Rosling devoted his professional life to global health, Global health problems, and how these are related to poverty. With the conviction that reason and knowledge improves the world and that we can eradicate extreme poverty and reduce CO2 emissions, Rosling pointed out that it is the richest billion of the earth's population that first and foremost must reduce CO2 emissions because they account for half of them.
Hans Rosling's memoirs How I Learned to understand the world, written together with the journalist Fanny Härgestam, was published posthumously in 2017 and Factfulness, written in collaboration with Ola and Anna Rosling Rönnlund, released in 2018.
Burial site: 0116-0836B
Image description: Hans Rosling, press Photo. Photo: Stefan Nilsson / Gapminder.org. [The image is cropped]
Click here for an uncropped image